MUSCLE TISSUE

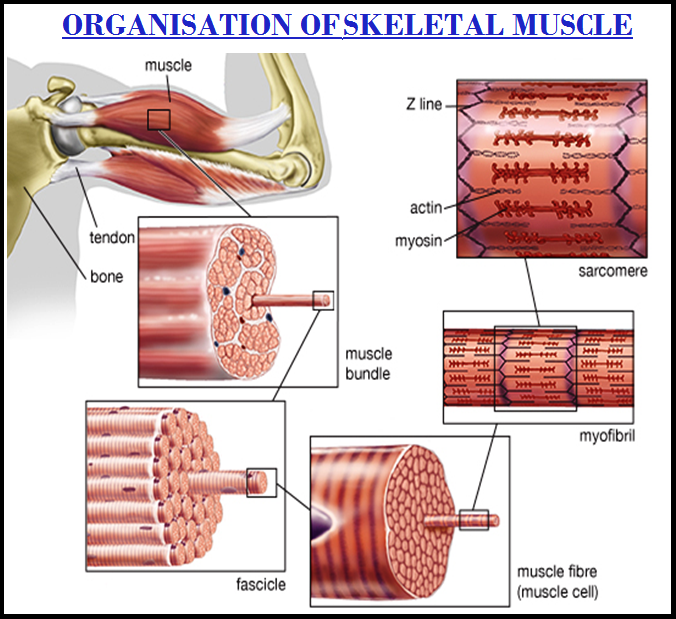
● `color{violet}("Each muscle")` is made of many `color{violet}("long, cylindrical fibres")` arranged in parallel arrays.
● These `color{violet}("fibres")` are composed of numerous fine fibrils, called `color{brown}("myofibrils.")`
● `color{violet}("Muscle fibres")` contract (shorten) in response to stimulation, then relax (lengthen) and return to their uncontracted state in a `color{violet}("coordinated fashion.")`
● Their action moves the body to adjust to the changes in the environment and to maintain the positions of the various parts of the body.
● In general, `color{violet}("muscles")` play an active role in all the movements of the body.
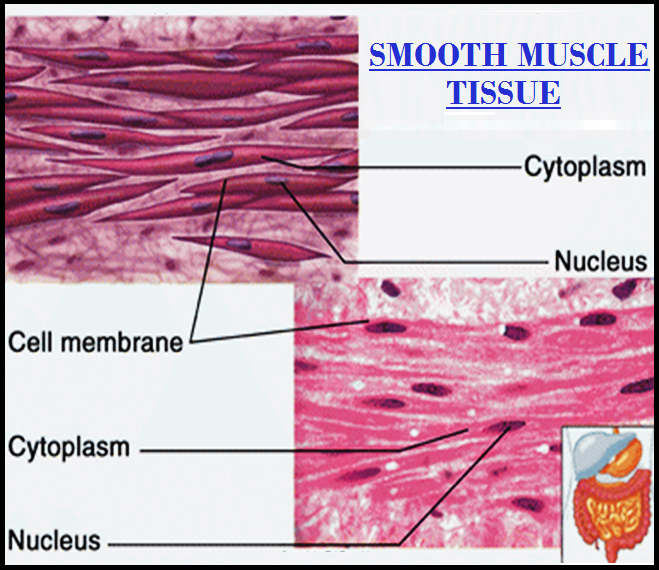
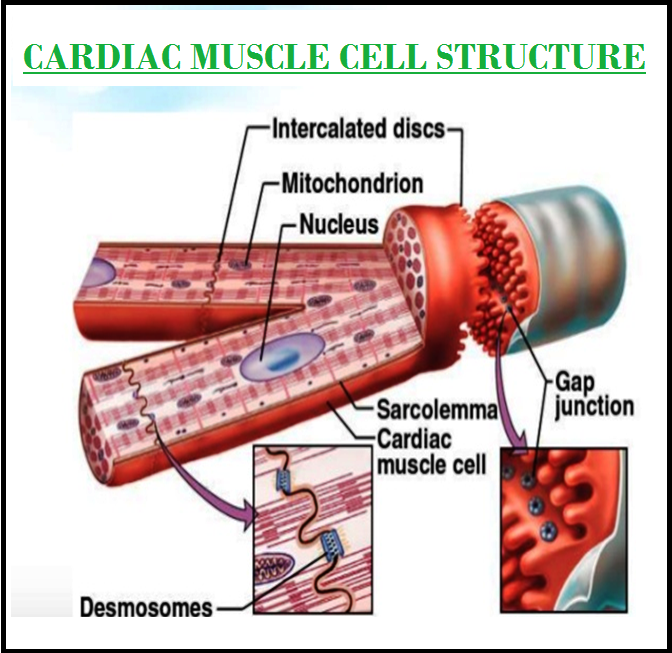
● `color{violet}("Muscles")` are of three types, `color{brown}("skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.")`
● These `color{violet}("fibres")` are composed of numerous fine fibrils, called `color{brown}("myofibrils.")`
● `color{violet}("Muscle fibres")` contract (shorten) in response to stimulation, then relax (lengthen) and return to their uncontracted state in a `color{violet}("coordinated fashion.")`
● Their action moves the body to adjust to the changes in the environment and to maintain the positions of the various parts of the body.
● In general, `color{violet}("muscles")` play an active role in all the movements of the body.
● `color{violet}("Muscles")` are of three types, `color{brown}("skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.")`